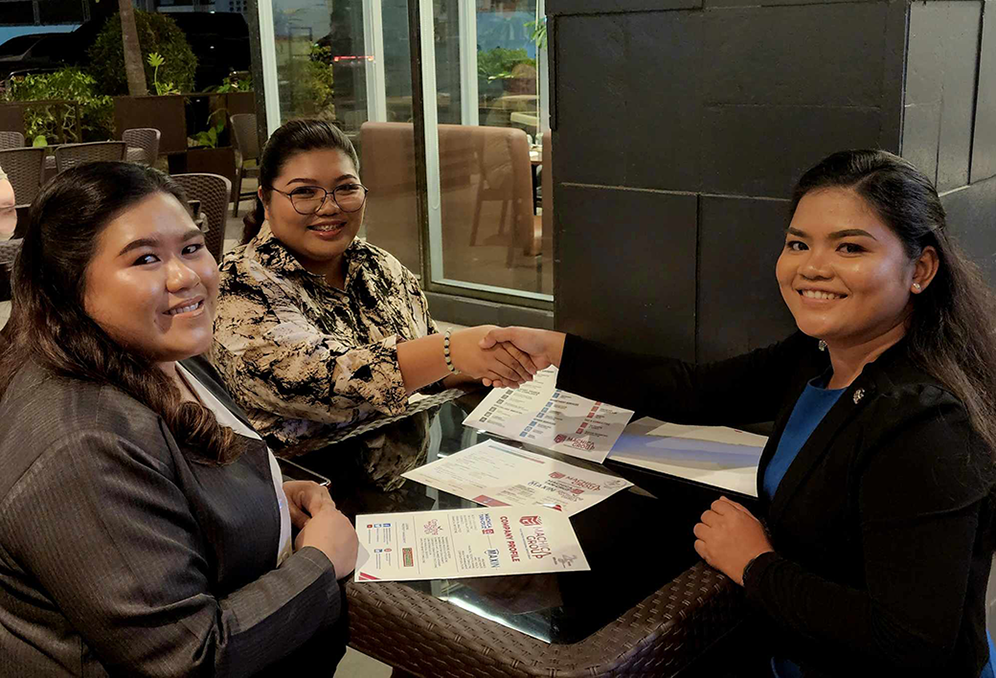
Corporate Formation and Structuring Services
Establish or Structure Your Business Entity with Confidence
From company registration to strategic structuring, we guide you through every step.
Corporate Formation and Structuring
The process includes registering with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) for corporations, the Department of Trade and Industry (DTI) for sole proprietorships, and obtaining necessary permits from local government units (LGUs) and the Bureau of Internal Revenue (BIR). Structuring involves setting up the company’s internal governance, defining shareholder roles, and drafting essential documents like bylaws and articles of incorporation. Proper formation and structuring ensure compliance, mitigate risks, and optimize operational efficiency for businesses in the Philippines.

Corporate Formation Services

Business Registration
From securing your business name to obtaining the necessary permits and registrations with government agencies, our comprehensive services ensure a smooth and hassle-free process for setting up your business in the Philippines. Whether you're forming a sole proprietorship, partnership, or corporation, we handle all the paperwork, so you can focus on growing your business. This may apply to domestic entity or foreign entity doing business in the Philippines.
Licensing and Permits
Navigating the landscape of business licenses and permits can be complex. Our expert team simplifies the process for you by handling all necessary applications and approvals to ensure your business complies with national and local regulations. From securing barangay clearances and Mayor's Permits to registering with the Bureau of Internal Revenue (BIR) and other relevant agencies, we take care of every detail, allowing you to focus on growing your business with peace of mind.

Compliance Support
Ensuring your business stays compliant with all legal requirements is crucial for long-term success. Our team offers comprehensive support in meeting regulatory obligations, such as filing annual reports, renewing business permits, and staying updated with the latest government regulations. We help you navigate the complexities of compliance, so you can focus on growing your business with confidence.

