Dr. Michael A. Machica, the Managing Partner and Chairman of Machica Tan-Cruz & Co., CPAs, imparts his knowledge on Transfer Pricing during the Philippine Tax Congress held at Crowne Plaza Galleria on December 9, 2017.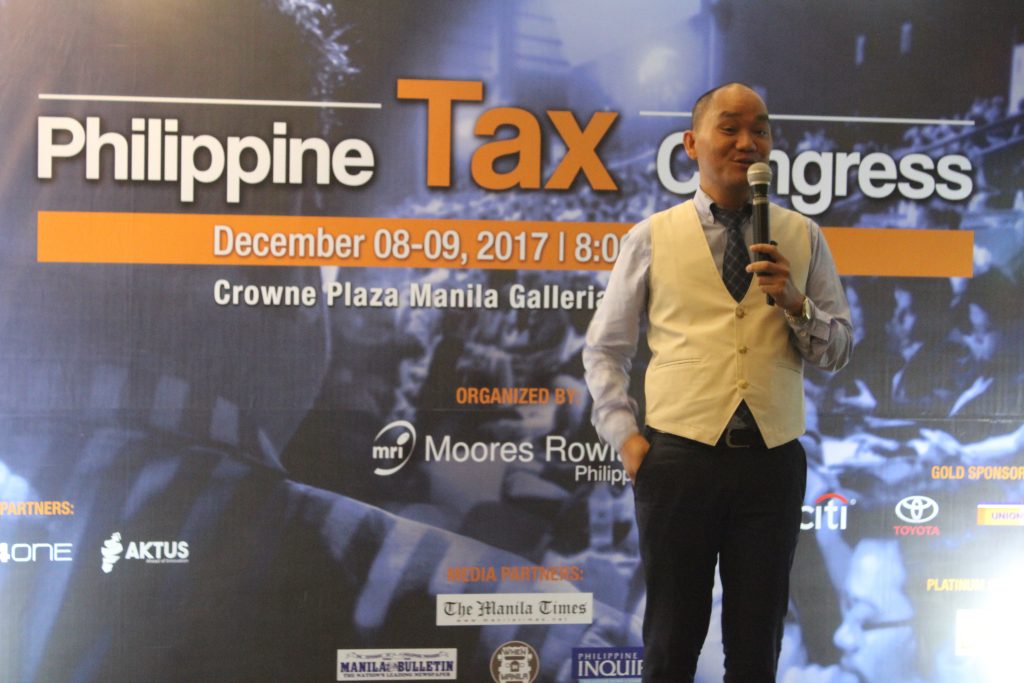 Spearheaded by the Moores Rowland PH – Professionals of the Future (MRP-POF), the event takes off with the objective of providing various professionals an avenue for comprehensive learning and career development. In view of this, Dr. Machica focuses his lecture on the latest updates and practical guides in transfer pricing for multinational enterprises.
Spearheaded by the Moores Rowland PH – Professionals of the Future (MRP-POF), the event takes off with the objective of providing various professionals an avenue for comprehensive learning and career development. In view of this, Dr. Machica focuses his lecture on the latest updates and practical guides in transfer pricing for multinational enterprises.
 As the congress culminates, POF achieves another milestone as it publishes ‘50 Inspiring Accountants’ – a book featuring narratives of professionals’ success, including that of Dr. Machica.
As the congress culminates, POF achieves another milestone as it publishes ‘50 Inspiring Accountants’ – a book featuring narratives of professionals’ success, including that of Dr. Machica.
Machica Tan-Cruz & Co. is a progressive full-service accounting firm with offices in Makati, Manila, and Tacloban. It is the Philippine member firm of the LEA Global and the Dezan Shira Asian Alliance. Dr Machica is the firm’s lead partner for transfer pricing, international tax, and corporate advisory services. He was recognized by the ACQ Global Awards as the Philippine Transfer Pricing Advisor of the Year 2017.